The logistics Industry trends rely on dramatic developments driven by introducing technologically driven advances in business processes. The next-gen Logistics management is heading towards a more customer-centric and competitive global supply chain. Automation of logistic operations has resulted in a substantial improvement in output and workflow reliability. Improving the supply chain’s transparency and traceability is crucial to ensure a flexible and dynamic relationship with stakeholders. According to Statista, third-party logistics is a growing industry in the United States with total industry revenue reached 212.8 billion U.S. dollars.
Top 10 Logistics Industry Trends in 2021

1. Internet of Things
The Internet of Things is communication between physical devices that track and transmit data through the Internet and without human interference. IoT is the #1 logistics industry trend that increases visibility at any level of the supply chain and boosts inventory management performance. The Internet of Things is communication between physical devices that track and transmit data through the Internet and without human interference. IoT in logistics increases visibility at any level of the supply chain and boosts inventory management performance.
2. Artificial Intelligence
AI algorithms combined with machine learning service providers to be pragmatic in coping with spikes in demand. For example, AI-based planning solutions allow managers to schedule supply chain operations and identify ways to reduce operational costs. Self-driving AI and intelligent road technology are affecting a positive change towards service automation. Besides, AI-based cognitive automation technology brings knowledge to simplify administrative processes and accelerates information-intensive operations.
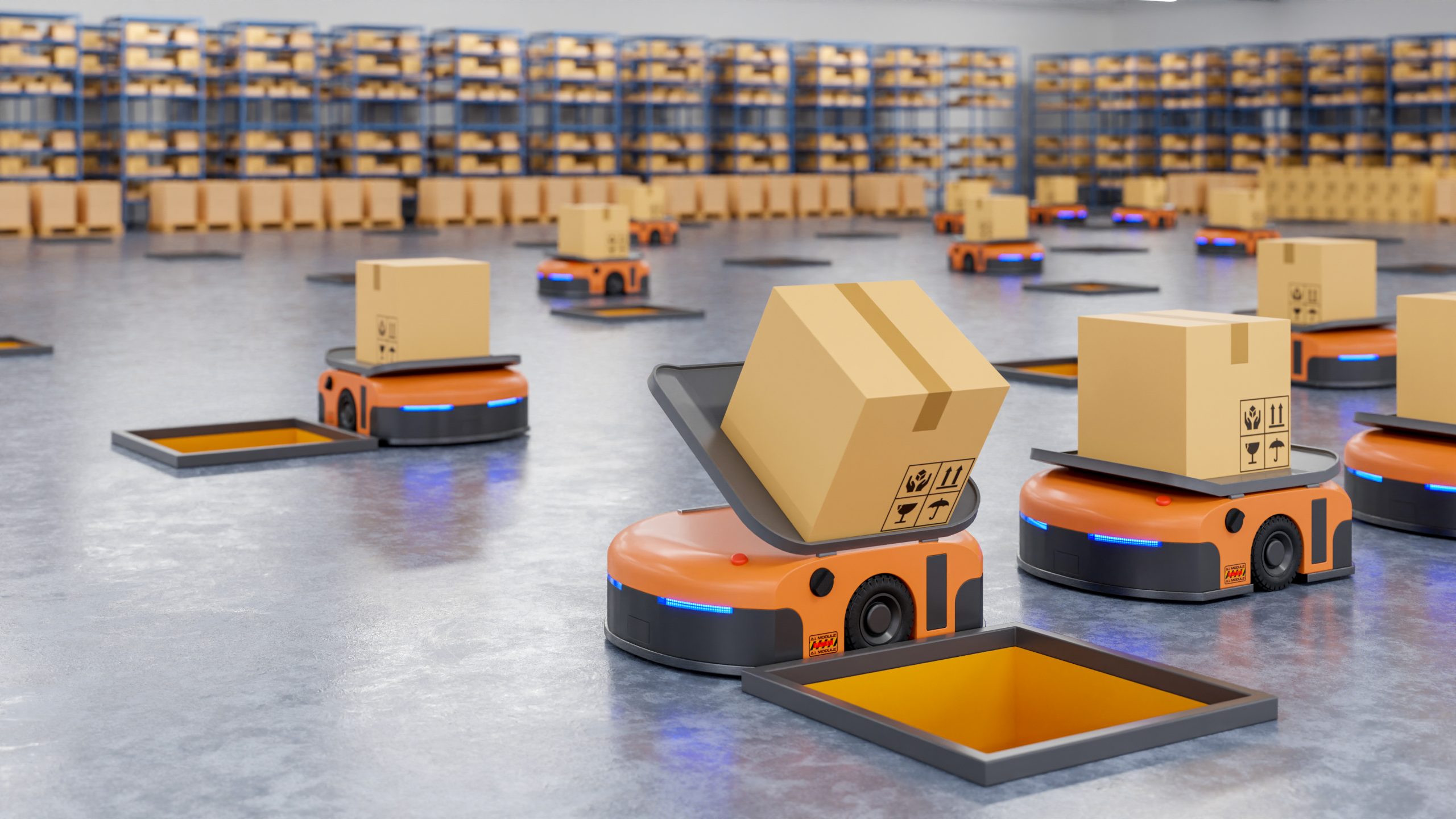
3. Robotics
Integrating robots in logistics industry trends improves the speed and precision of supply chain operations and decreases human error. Robots provide more uptime and enhance productivity relative to human jobs. Robots, however, do not take up human positions but rather work collaboratively with them to maximize productivity. Physical robotics, such as collaborative robots (co-bots) and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), are used to collect and move goods in warehouses and storage facilities. Besides, software robots perform routine and mundane activities that open up time for human jobs.
4. Last-Mile Delivery
The last step in the supply chain, from the factory or delivery center to the consumer, is always inefficient and often includes a large part of shipping products’ overall cost. Last-mile distribution is the most critical aspect of logistics as it contributes directly to customer loyalty. However, last-mile distribution faces several challenges, including disruptions due to road congestion, consumer nuances, government regulation, and delivery speed.
5. Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation increases efficiency, speed, and competitiveness by reducing human interaction. Pick and position technologies such as automated guided vehicles, robotic pick-up, automated storage and recovery, and put-wall pick-up eliminate error rates and improve warehouse efficiency. Warehouses require a mix of robust automation systems to manage running logistics costs.
6. Blockchain
Blockchain provides authentication through a shared ledger structure and solves urgent traceability and related problems. This structure gives accountability of transactions to the whole logistic process. Also, smart contracts built on blockchain technologies allow for faster certification and clearance by reducing processing times at checkpoints.

7. Big Data & Data Analytics
Data analytics offer useful insights for improving warehouses’ efficiency, managing production, and optimizing the usage of logistical services. The data collected from the monitoring role and conditions and fleet schedules help refine routes and distribution preparation. The study of business data facilitates the further improvement of supplier prices, inventory levels, and risk management reporting. Also, sophisticated analytics offer information that helps detect anomalies and provide predictive maintenance solutions.
8. Cloud Computing
Cloud-based SaaS applications for logistics organizations allow for pay-per-use models requiring low capital investment. This technology minimizes the expense and costs of managing the IT facilities. Cloud-based logistics systems also overcome connectivity gaps and allow businesses to communicate and safely exchange data. Also, cloud integration facilitates data collection from control systems to evaluate total logistic operations. Finally, cloud-integrated logistics provides universal connectivity and is not limited to any physical space.

9. Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles improve road safety and distribute goods efficiently by eliminating human error when driving. They maximize reliability in the first and last-mile supply as they are built to run all day and all night. Autonomous vehicles increase fuel efficiency by using plating methods for long-distance routes, reducing traffic congestion, and improving travel routes by taking advantage of AI.
10. Elastic Logistics
Elastic logistics allows businesses to manage supply chain processes more efficiently during times of fluctuations in demand. It helps upscale or downscale supply chain operations, depending on market demand, as needed. Elastic logistics thus tackle supply chain firms’ problems, including under-use of vessels, storage shortages, and over-stocking.
What Does This Mean For Logistics Companies?
With consumer demands increasingly growing and interests are changing towards product diversity and tailored services, the logistics and supply chain industries are under pressure. Rapid advances in new technology such as the Internet of Things, advanced mobile robotics, artificial intelligence, and blockchain-enabled applications lead to the challenges of choosing the perfect fit. As technological development progresses, new businesses must be cautious and detect potentially disruptive consequences sooner.
The disruption fields highlighted in this report on 10 Logistics Market Developments are scratching the surface of what we find during our study. Logistics as a business, cloud logistics, automated identifiers, and additive manufacturing are all fields that have a massive effect on logistics businesses in one direction or another. Identifying new markets and evolving technology for early implementation of the market is a long way to achieve a strategic edge and become a pioneer in the industry.