In the GIS world, there are two primary data formats one is a vector, and another one is raster data formats. Raster data is a representation of images in rows and columns of pixel format, and it is a continuous data representation. Vector data is the representation of spatial features in points, lines & polygon formats, and it is a discrete data representation.
What is Spatial Data?
Spatial data is the physical representation of earth features. It represents the location, size, and shape of the object in the earth i.e., building, ponds, mountains, administration, boundaries, etc.
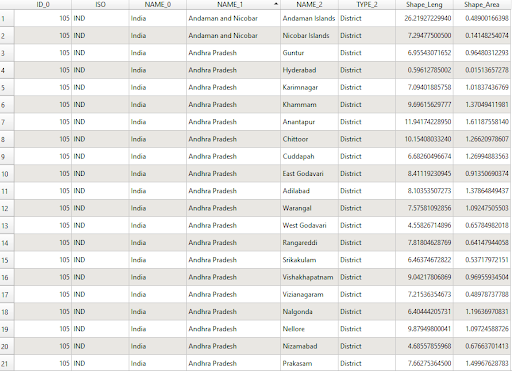
Spatial Data is available in two primary formats 1. Vector and, 2.Raster
Raster
A raster data is a representation of images in a matrix of cells/ pixels into rows and columns. The raster data set and data values are stored in rows and columns. To have high accuracy data, GIS professionals use high-resolution raster datasets. As it comes with the own challenges and difficulties to manage, Map info advancement introduces to a specially designed data format, multi- Resolution Raster (MRR).
There are different raster types, Image, Image Palette, Classified and Continuous, or discrete. These types are stored as two significant formats, single color data, and composite color data.
The image field type is used to store the single color data band, suppose the composite color data(RGB) is stored. It represents in a virtual band format. Image palette field types have a color palette, the storage of a single data band indicates in the color palette. If the composite color data type (like RGB), it represents a virtual band.
Classified field type contains a classification table, a single data band stores the indices of the classification table. The classification table is represented as a virtual band, and the table contains any kind of virtual data that includes strings. It has no structural requirements or imposition of limits (except the limitation of four billion (approximation) number entries in the table.
Continuous/Discrete field types containing data are in one or more bands. Each of the constant/discrete band data types may have unique data types. Some of the data type components, such as multi-component color or complex numbers, are available in the virtual band. All fields of raster files (bands) share a coordination system-defined file.
Popular Raster file formats
- Portable Network Graphics (PNG)
- Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG2000)
- JPEG File Interchange Format (JFIF)
- Multi-resolution Seamless Image Database (MrSID)
- Network Common Data Form (netCDF)
- Digital raster graphic(DRG)
- ARC Digitized Raster Graphic (ADRG)
- Enhanced Compressed ARC Raster Graphics (ECRG)
- Compressed ARC Digitized Raster Graphics (CADRG)
- Raster Product Format (RPF)
- Binary file – Band Interleaved by Pixel (BIP), Band Interleaved by Line (BIL), Band Sequential (BSQ)
- Enhanced Compressed Wavelet (ECW)
- Extensible N-Dimensional Data Format (NDF)
- GDAL Virtual Format (VRT)
- Tagged Image File Formats (TIFF)
- Geo Tagged Image File Formats (GeoTIFF)
- Graphic Interchange Format (GIF)
- Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
- RS Landsat
- ArcInfo Grid
- Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar (AIRSAR) Polarimetric
- Bitmap (BMP), device-independent bitmap (DIB) format, or Microsoft Windows bitmap
- BSB
- Controlled Image Base (CIB)
- Digital Geographic Information Exchange Standard (DIGEST)
- File geodatabase
- ENVI Header
- Golden Software Grid (.grd)
- GRIB
- Hierarchical Data Format (HDF) 4
- HGT
- High-Resolution Elevation (HRE)
- Integrated Software for Imagers and Spectrometers (ISIS)
- Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM)
- Terragen terrain
Vector
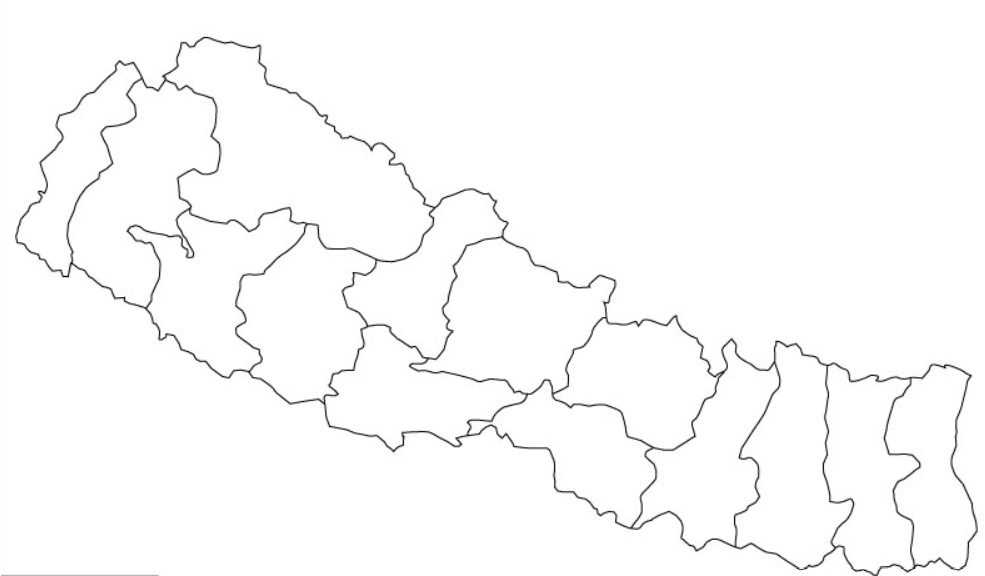
Vector data are represented in lines and polygons. Polygons are used to describe areas such as the boundary of a city (on a large scale map), forest, and lakes. Polygon features are two dimensional. It can be used to measure the area and perimeter of a geographic feature.
Line data represents the linear features. Some Common examples for the representation of line features are rivers, roads, etc. The line is a one-dimensional representation. It gives only the length of the element.
Point data is used to represent non-adjacent features and to represent discrete data points. Points have zero dimensions, and it gives latitude & longitude of the respective location. The point feature will not provide the length and area of the features. Examples would be schools, points of interest such as hospitals, schools, colleges, worship centers, and more other locations.
Popular Vector file formats
- Shapefiles
- ArcInfo Coverage
- E00 ArcInfo Interchange
- Spatial Database engine (ArcSDE)
- Digital Line Graph (DLG)
- GeoJSON
- AutoCAD DXF
- Keyhole Markup Language (KML)
- TIGER
- Vector Product Format (VPF)
- Esri TIN
- Geography Markup Language (GML)
- SpatiaLite
- OSM (OpenStreetMap)
- Scalable Vector Graphics
- National Transfer Format (NTF)
- SOSI
- MapInfo TAB format
- GPS eXchange Format (GPX)
- IDRISI Vector
- Geographic Base File-Dual Independent Mask Encoding (GBF-DIME)
- Delimited Text Files
Also Read
What is Non-spatial Data?
Non-spatial data are represented in table formats. For example, the administrative boundary table has population information, district name, provinces, sex ratio, etc.
Popular Database
- PostgreSQL
- SpatiaLite
- MSSQL
- Oracle
- SQL
- ESRI Geodatabase
Other than spatial & non-spatial data formats, Other different formats are used in GIS.
Web File Formats
To visualize the geographic features over the internet. The geographic features have some specific data formats. Although other web-based file formats store geographic data (such as GeoJSON), these file formats are unique to web mapping.
Popular Web file formats
- GeoRSS
- Web Feature Service (WFS)
- Web Map Service(WMS)
- (WMTS )Web Map Tile Service
- Web Coverage Service(WCS)
- Esri ArcGIS Online Web Services
Interchange file formats
The purpose of interchange file formats is to transfer files between different software. It is specially designed for interoperability and data transfer.
Popular Interchange file formats
- Esri ArcInfo Export (Interchange)
- MapInfo Interchange File
- Map Package
3D File Formats
Three-dimensional file formats are the representation of spatial extent, i.e. (latitude & longitude information ), the elevation information (visualization of depth and height of the terrain). These 3D file formats are graphic representations of objects in the real world developed in 3D modeling software.
Popular 3D File Formats
- 3D Studio Max.
- VRML or GeoVRML.
- OpenFlight.
- Collada.
- Wavefront OBJ model.
- Trimble Sketchup
RELATED POSTS
- Image Classification Techniques in Remote Sensing
- What is LiDAR Technology And How Does It Work?
- Forest Fire Detection Using Remote Sensing Techniques
- Top 10 Topographic Maps From Around the World
- Geographical Information System (GIS) in Urban Planning
Looking for more? Subscribe to weekly newsletters that can help your stay updated on Geographic Information Systems and Application developments.